Unit 5.1 Exponents
Exponents
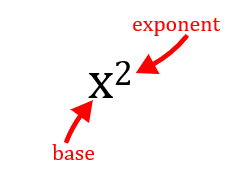
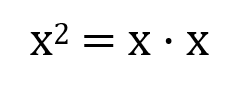
Product Rule
To multiply the same bases with different exponents, add the exponents
xa · xb= x(a+b)
Product Rule
x5 · x6 = x(5+6) = x11
Quotient Rule
To divide the same base with different exponents, subtract the exponents
[latex]\frac{x^a}{x^b}[/latex]= x(a - b)
Quotient Rule
[latex]\frac{x^5}{x^3}=x^{5-3}=x^2[/latex]
Power Rule
When you have a power to a power, multiply the powers
(xa)b = xa · b
Power Rule
(x3)4 = x3 · 4 = x12
Power of a Product
Distribute the exponent across each term of the monomial
(xy)a = xaya
Power of a Product
(xy)5 = x5y5
This law also allows you to factor out exponents
x8y4 = (x2y)4
Power of a Quotient
Distribute the exponent to both the numerator and denominator
[latex]\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{y}}\right)^\mathrm{a}\mathrm{=} \frac{x^a}{y^a}[/latex]
Power of a Quotient
[latex]\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{y}}\right)^\mathrm{2}\mathrm{=} \frac{x^2}{y^2}[/latex]
Zero Exponent Law and Identity Law
Zero Exponent Law: Any value to a 0 exponent is equal to 1
Identity Law: Any value with an exponent of 1 is equal to that value
x0 = 1
x1 = x
Negative Exponent Rule
Any value to a negative exponent is the reciprocal of that number
x-1 =[latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex]
Negative Exponent Rule
Example 1:
[latex]\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{-4}}\mathrm{=\ }\frac{\mathrm{1} }{\mathrm{x}^\mathrm{4}}[/latex]
Example 2:
[latex]\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{-4}}}\mathrm{\ =\ }x^4[/latex]