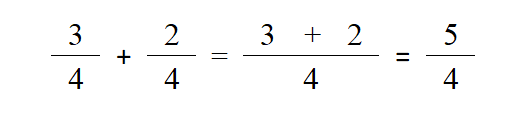Unit 1.5: Fractions
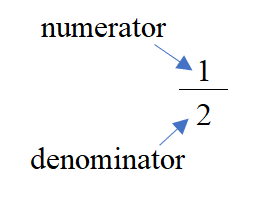
Fractions
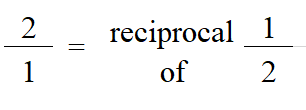
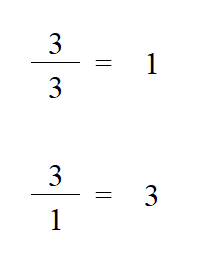
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
To multiply fractions, you multiply the numerator of the first fraction by the numerator in the first fraction and that is over the two denominators together. Then simplify if required
Multiplying Fractions
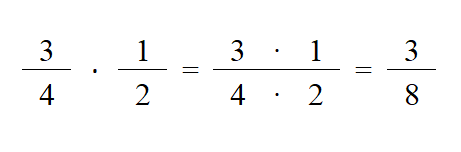
To divide fractions, you multiply by the reciprocal of the second fraction then simplify
Dividing Fractions
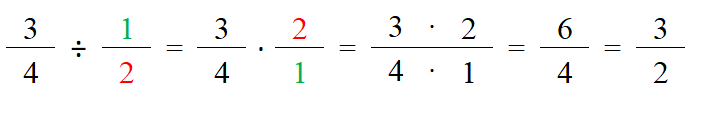
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
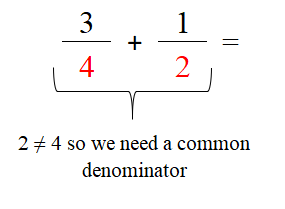
To add or subtractions together, you MUST find a common denominator (i.e. the denominators are the same). With multiplication, you can multiply straight across but you cannot add the fractions together without a common denominator
Adding Fractions
1. Determine if you need a common denominator
2. Use Least Common Multiple (LCM) to find the smallest number that both numbers can go into. In this case, 2 can go into 4 so we’re only going to transform one of the fractions. In order to make 2 (the denominator of 1/2) into 4, we need to multiply by 2. We don’t want to change the value of the fraction, just the scale, so we multiply both the numerator and denominator by 2
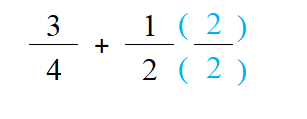
3. Now 1/2 becomes 2/4 which makes it a common denominator and now we can add or subtract the numerators
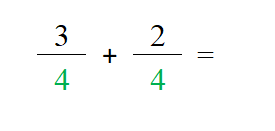
4. It is important to note that you only add the numerators, the denominator remains the same