Unit 1.1: Division
Dividing Whole Numbers
Dividing numbers is the process of seeing how many times a number can fit into another number. The smaller number is called the divisor and the larger is the dividend. For example, if we wanted to see how many times 5 can fit into 15 we would write 15 ÷ 5 which gives us 3. From our example in multiplication, we know that it takes 3 of the number 5 to get to 15.
Example: Long Division
267 ÷ 23 = ???
1. Start by putting the larger number (dividend) into a little “house” called the “vinculum” and the smaller number (divisor) outside of it
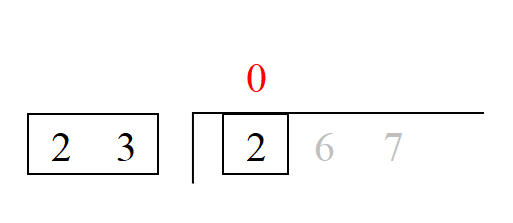
2. Look at the divisor and the first highest number of the dividend. How many times does the divisor go into the first number? 23 does not go into 2 at all since 23 > 2
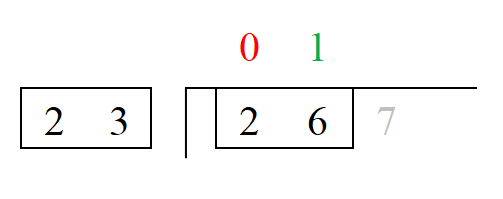
3. We need to include the second number of the dividend. That makes it 26. Since 23 < 26, it is divisible. 23 only goes into 26 1 time evenly so we write a 1 on top of the house in the 10s place.
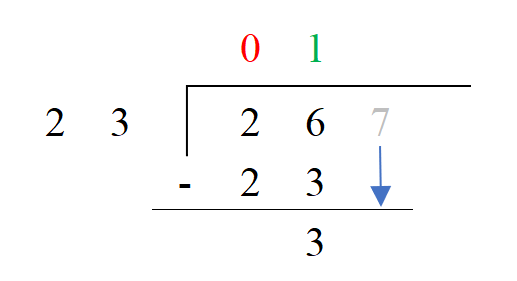
4. Subtract the divisor from the augmented dividend. In this case it is 26 – 23 = 3. We still need to deal with the 7 so we will drop it down.
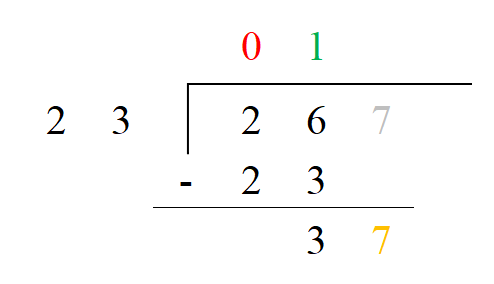
5. Look at the new value under the line and see how many times the divisor will go into that number. Since 23 < 37, it is divisible but it only goes into it one time. We write another 1 on top of the house in the ones place.
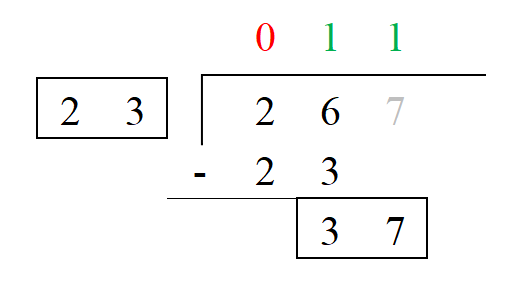
6. Subtract the divisor value from 37. This gives us 14. Since 14 < 23, we cannot divide further
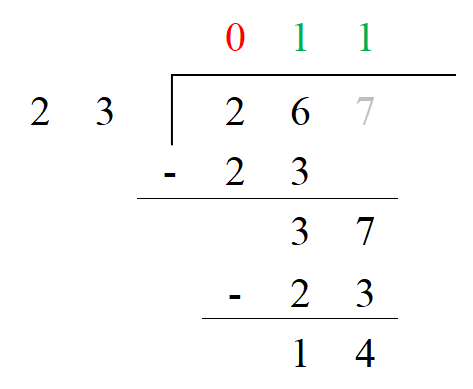
7. The answer would be 11 with a remainder of 14 or 11 with 14/23 left over.
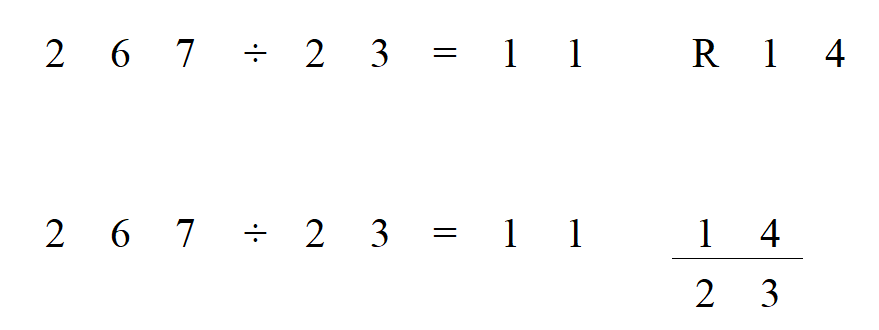
So 654 x 31 = 11 R 14
Dividing Negative Numbers
Dividing 2 negative numbers will result in a positive number
Dividing a positive number by a negative number will result in a negative number
Dividing a negative number by a positive number will result in a negative number