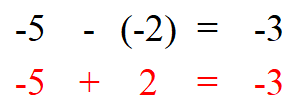Unit 1.1: Subtraction
Subtracting Whole Numbers
Subtraction is the process we use to take away one number from another number. We are concerned with what is left over.
Example: Subtraction
112 – 49 = ?
1. Start by writing the larger number on top with the ones, tens, hundreds (thousands, etc.) places lined up with the number below
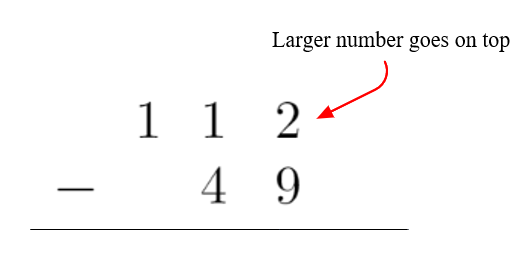
2. Subtract the right most digits, in the ones place (since 2<9, we must borrow from the 1 to the left of it)
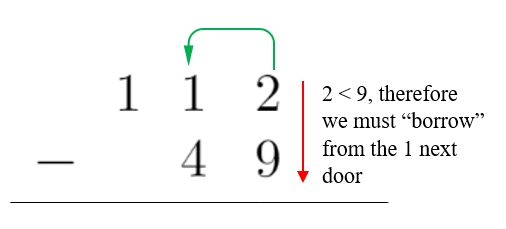
3. Borrow 1 from the digit to the left by reducing the value by one. Since this digit was 1 already, it becomes zero (1 – 1 = 0)
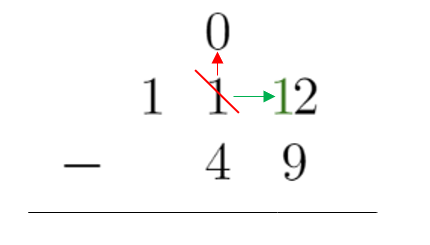
4. After borrowing a 1 from the digit to the left, we are able to subtract since the 2 becomes 12. We write that in the ones place under the line
12 – 9 = 3
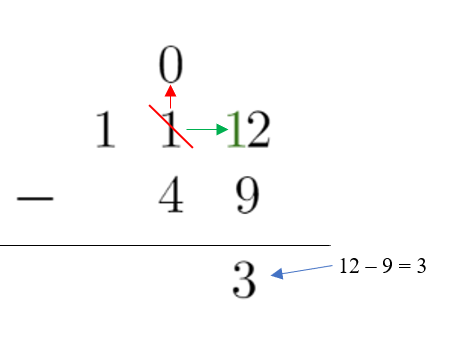
5. Since the digit in the tens place is now zero, and 0 < 4, we need to borrow from the digit to the left again.
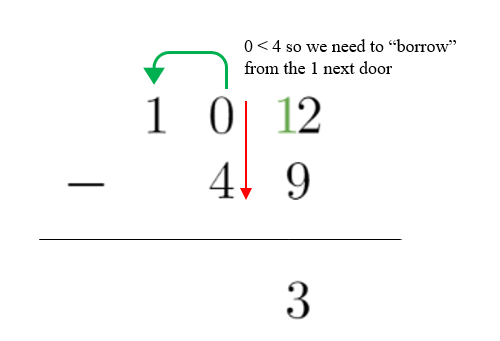
6. Borrow 1 from the digit to the left by reducing the value by one. Since this digit was 1 already, it becomes zero (1 – 1 = 0)
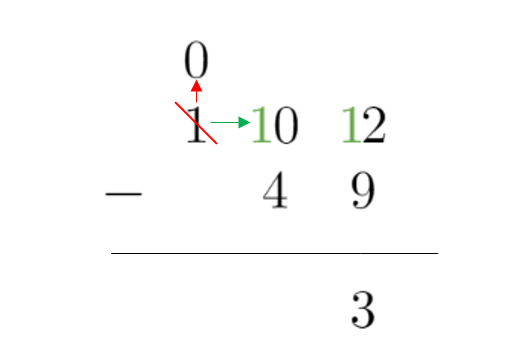
7. After borrowing a 1 from the digit to the left, we are able to subtract since the 0 becomes 10. We write that in the tens place under the line
10 – 4 = 6
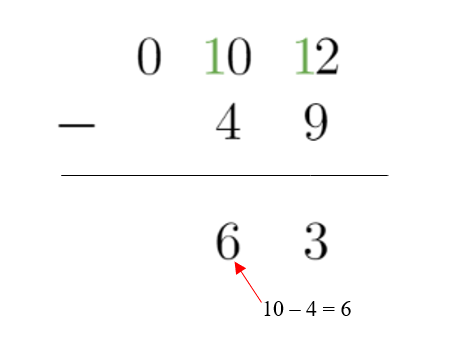
Since the hundreds place is already zero, we don’t have anything left to subtract.
So 112 – 49 = 63
Subtracting Negative Numbers
Subtracting two negative numbers together will result in a smaller positive number, think of it like adding a negative number to a positive number. The negative signs “cancel out”