Chapter 10 Plate Tectonics

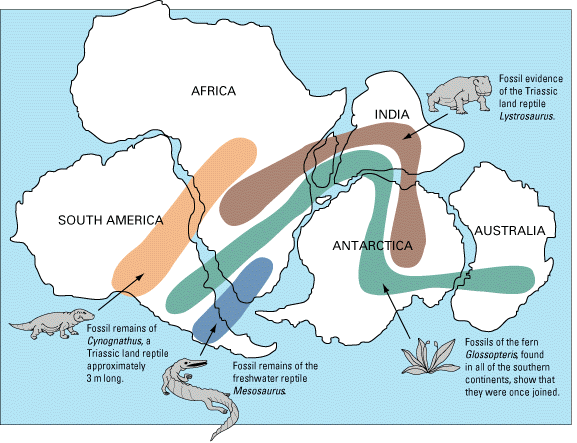
Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) (Figure 10.1.1) earned a PhD in astronomy at the University of Berlin in 1904, but he had always been interested in geophysics and meteorology and spent most of his academic career working in meteorology. In 1911 he happened on a scientific publication that included a description of the existence of matching Permian-aged terrestrial fossils in various parts of South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia (Figure 10.1.2).
Wegener concluded that this distribution of terrestrial organisms could only exist if these continents were joined together during the Permian, and he coined the term Pangea (“all land”) for the supercontinent that he thought included all of the present-day continents.
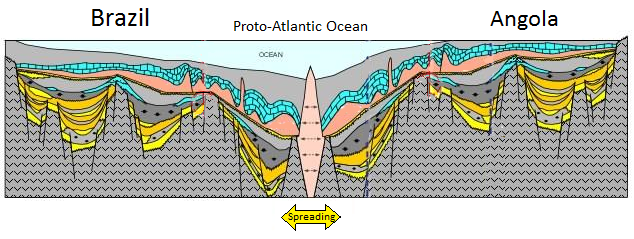
Wegener pursued his theory with determination—combing the libraries, consulting with colleagues, and making observations—looking for evidence to support it. He relied heavily on matching geological patterns across oceans, such as sedimentary strata in South America matching those in Africa (Figure 10.1.3), North American coalfields matching those in Europe, and the mountains of Atlantic Canada matching those of northern Britain—both in morphology and rock type.
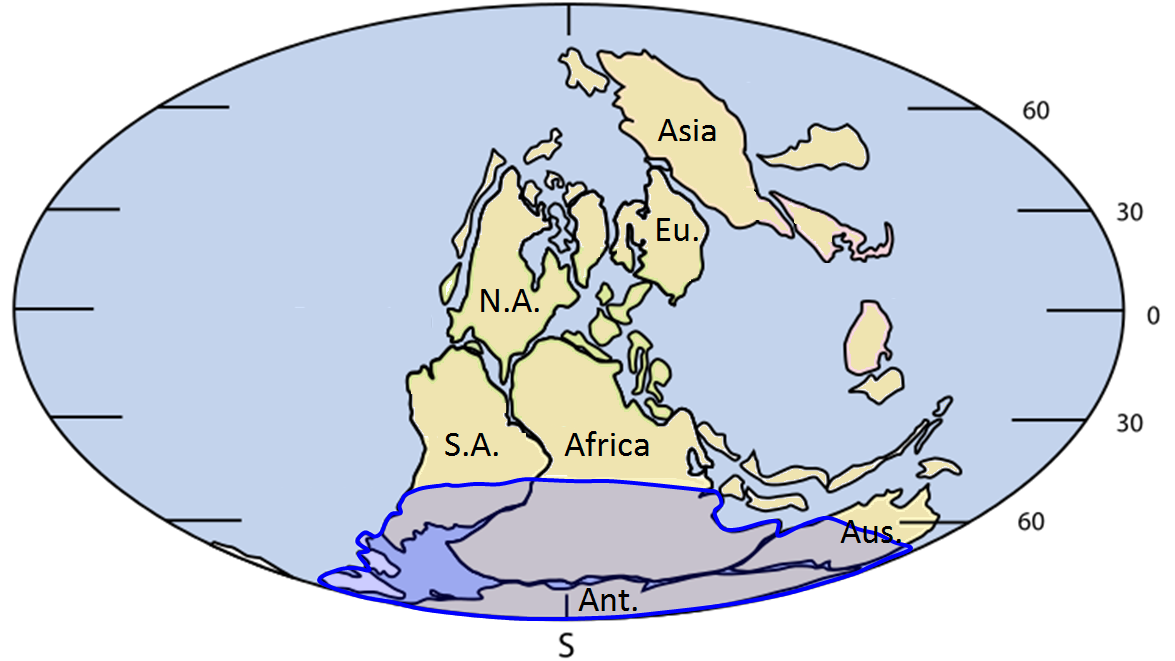
Wegener referred to the evidence for the Carboniferous and Permian (~300 Ma) Karoo Glaciation in South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia (Figure 10.1.4). He argued that this could only have happened if these continents were once all connected as a single supercontinent. He also cited evidence (based on his own astronomical observations) that showed that the continents were moving with respect to each other, and determined a separation rate between Greenland and Scandinavia of 11 metres per year, although he admitted that the measurements were not accurate. In fact they weren’t even close—the separation rate is actually about 2.5 centimetres per year!
Wegener first published his ideas in 1912 in a short book called Die Entstehung der Kontinente (The Origin of Continents), and then in 1915 in Die Entstehung der Kontinente und Ozeane (The Origin of Continents and Oceans). He revised this book several times up to 1929. It was translated into French, English, Spanish, and Russian in 1924.
In fact the continental fits were not perfect and the geological matchups were not always consistent, but the most serious problem of all was that Wegener could not conceive of a credible mechanism for moving the continents around. It was understood by this time that the continents were primarily composed of sialic material (SIAL: silicon and aluminum dominated, similar to “felsic”), and that the ocean floors were primarily simatic (SIMA: silicon and magnesium dominated, similar to “mafic”). Wegener proposed that the continents were like icebergs floating on the heavier SIMA crust, but the only forces that he could invoke to propel continents around were poleflucht, the effect of Earth’s rotation pushing objects toward the equator, and the lunar and solar tidal forces, which tend to push objects toward the west. It was quickly shown that these forces were far too weak to move continents, and without any reasonable mechanism to make it work, Wegener’s theory was quickly dismissed by most geologists of the day.
Alfred Wegener died in Greenland in 1930 while carrying out studies related to glaciation and climate. At the time of his death, his ideas were tentatively accepted by only a small minority of geologists, and soundly rejected by most. However, within a few decades that was all to change. For more about his extremely important contributions to Earth science, visit the NASA website to see a collection of articles on Alfred Wegener.
Image Descriptions
Figure 10.1.2 image description: Fossils found across different continents suggest that these continents were once joined as a super-continent. Fossil remains of Cynognathus (a terrestrial reptile) and Mesosaurus (a freshwater reptile) have been found in South America and Africa. Fossil evidence of the Lystrosaurus, a land reptile from the Triassic period, has been found in India, Africa, and Antarctica. Fossils of the fern Glossopteris have been found in Australia, Antarctica, India, Africa, and South America. When you position these continents so they fit together, the areas where these fossils were found line up. [Return to Figure 10.1.2]
Media Attributions
- Figure 10.1.1: “Alfred Wegener ca.1924-30.” Public domain.
- Figure 10.1.2: “Snider-Pellegrini Wegener fossil map” by Osvaldocangaspadilla. Public domain.
- Figure 10.1.3: © Steven Earle. CC BY. Based on “Angola -Brazil sub-sea geology” by Cobalt International Energy can be found at U.S. Energy Information Administration: Country Analysis Brief: Angola (May 2016) [PDF].
- Figure 10.1.4: “Karoo Glaciation” © GeoPotinga. Adapted by Steven Earle. CC BY-SA.
the supercontinent that existed between approximately 300 and 180 Ma
referring to rock or magma in which silica and aluminum are the predominant components (generally equivalent to felsic)
referring to rock or magma in which silica, magnesium and iron are the predominant components (generally equivalent to mafic)
