Chapter 3 The Origin of Earth and the Solar System
Karla Panchuk
The topics covered in this chapter can be summarized as follows:
| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| 3.1 Starting with a Big Bang | The universe began 13.77 billion years ago when energy, matter, and space expanded from a single point. Evidence for the big bang is the cosmic “afterglow” from when the universe was still very dense, and red-shifted light from distant galaxies, which tell us the universe is still expanding. |
| 3.2 Forming Planets from the Remnants of Exploding Stars | The big bang produced hydrogen, helium, and lithium, but heavier elements come from nuclear fusion reactions in stars. Large stars make elements such as silicon, iron, and magnesium, which are important in forming terrestrial planets. Large stars explode as supernovae and scatter the elements into space. |
| 3.3 How to Build a Solar System | Solar systems begin with the collapse of a cloud of gas and dust. Material drawn to the centre forms a star, and the remainder forms a disk around the star. Material within the disk clumps together to form planets. In our solar system, rocky planets are closer to the Sun, and ice and gas giants are farther away. This is because temperatures near the Sun were too high for ice to form, but silicate minerals and metals could solidify. |
| 3.4 Earth’s First 2 Billion Years | Early Earth was heated by radioactive decay, collisions with bodies from space, and gravitational compression. Heating melted Earth, causing molten metal to sink to Earth’s centre and form a core, and silicate melt to float to the surface and form the mantle and crust. A collision with a planet the size of Mars knocked debris into orbit around Earth, and the debris coalesced into the moon. Earth’s atmosphere is the result of volcanic degassing, contributions by comets and meteorites, and photosynthesis. |
Questions for Review
Answers to review questions can be found in Appendix 2.
- How can astronomers view events that happened in the universe’s distant past?
- In this image of three spectra, one is from the Sun, and the other two are from galaxies. One of the galaxies is the Andromeda galaxy. Which spectrum is from Andromeda?
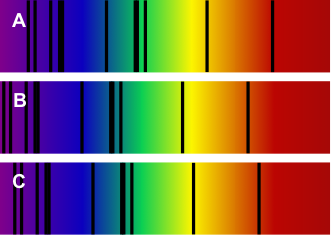
Figure A Spectra for the sun and two galaxies. - Astronomers looking for some of the earliest stars in the universe were surprised to find a planetary system called HIP 11952, which existed 12.8 billion years ago. This was very early in the universe’s history, when stars still consisted largely of hydrogen and helium. Do you think there were terrestrial planets in this system? Why or why not?
- Summarize the trends in size and composition of objects in the solar system.
- What is the frost line, and what does it help to explain?
- This cartoon shows three of the same type of solar system object. One goes on an adventure and comes back the worse for wear. What are the objects, and where might they be located?

Figure B Denizens of the solar system. - Why is Pluto not considered a planet?
- What is differentiation, and what must happen to a planet or asteroid for differentiation to occur?
- The exoplanet Kepler-452b is within the habitable zone of its star. In our solar system, planets a similar distance from the Sun are terrestrial planets. Why can we not say for certain that Kepler-452b’s distance from its star means it is a terrestrial planet?
- Of the planetary systems discovered thus far, none are exactly like our solar system. Does this mean our solar system is unique in the universe?
Media Attributions
- Figure A: © Karla Panchuk. CC BY.
- Figure B: “Oort Cloud” © Randall Munroe. CC BY-NC.
